Gamification is a powerful tool that has taken the world by storm, revolutionizing the way we approach engagement and motivation across various industries.
When done right, it has the power to drive people to achieve their goals, whether in the workplace, in the classroom, or in their personal lives. But why does it work? How does gamification motivate people to achieve their goals?
In simple terms, gamification uses relevant game design elements to engage and motivate people to achieve their goals. By adding elements of fun and competition, gamification can tap into our natural desire for social interaction and our love of games to drive us to achieve our goals.
To get a more detailed understanding of how gamification drives motivation, read the article below – it should have all the answers you’re looking for!
Understanding the Psychology of Gamification
As gamification is inextricably connected to the human mind, it is important to understand how the psychological elements of gamification work in order to design effective gamification systems.
Importance of Motivation in Human Behavior
Motivation is a driving force that influences human behavior, guiding our actions and decisions. It plays a critical role in determining the level of effort we put into tasks, the perseverance we exhibit when faced with challenges, and our overall performance.
By understanding the principles of motivation, gamification designers can create systems that effectively stimulate individuals to engage with activities, complete tasks, and achieve their goals.
Theories of Motivation
There are various psychological theories that help explain how motivation works. Two of the most widely recognized and applicable theories in gamification are Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and Self-Determination Theory.
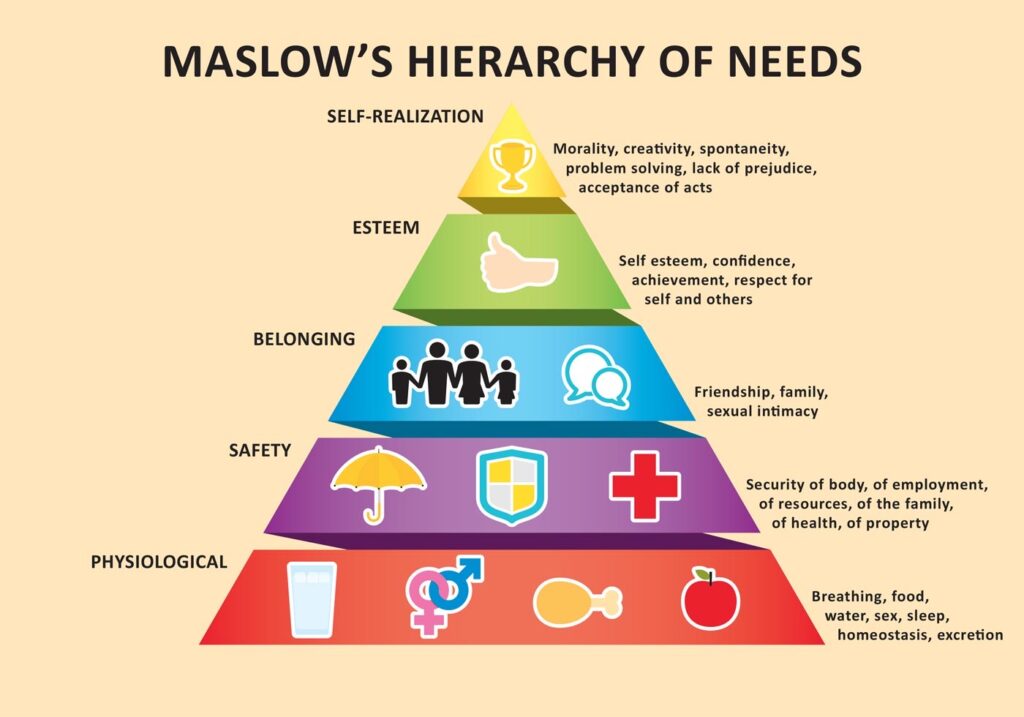
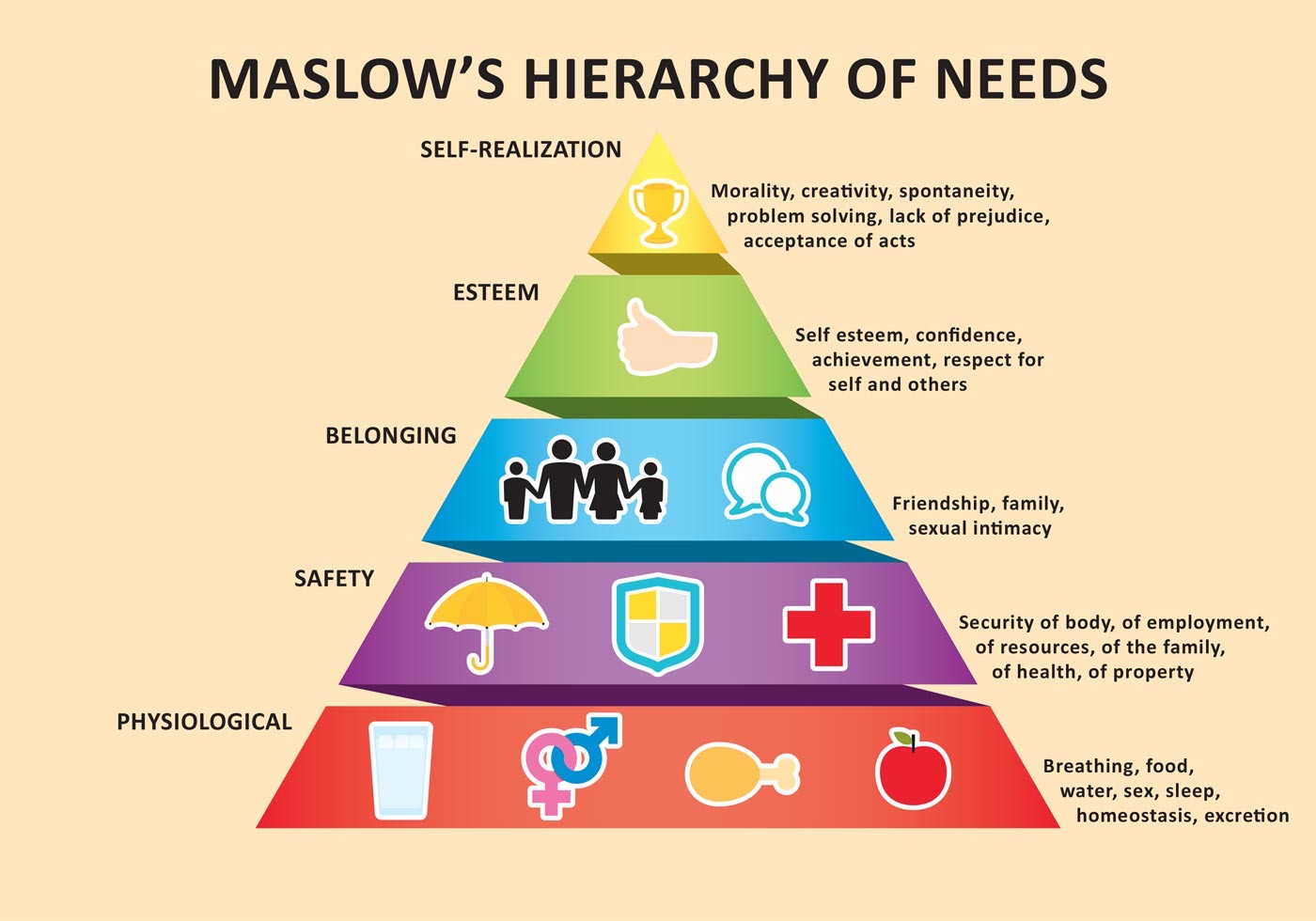
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Developed by psychologist Abraham Maslow, this theory suggests that humans have a hierarchy of needs that must be met for optimal well-being and motivation.
Basic physiological needs such as food, water, and shelter are at the base of the hierarchy, followed by safety, love and belonging, esteem, and self-actualization. Understanding this hierarchy can help gamification designers create experiences that address these needs, leading to increased motivation and engagement.
Self-Determination Theory
Another important theory in the context of gamification is Self-Determination Theory (SDT), developed by psychologists Edward Deci and Richard Ryan. SDT posits that humans have three innate psychological needs: autonomy, competence, and relatedness. When these needs are satisfied, individuals experience heightened motivation and optimal well-being.
| Psychological need | How does it work? | Relationship with gamification |
| Autonomy | People are motivated when they feel a sense of control over their actions and decisions. | Gamified activities providing choices and allowing users to set their own goals can enhance the feeling of autonomy. |
| Competence | Individuals are driven to improve their skills and abilities. | Gamification systems can foster competence by setting challenging tasks and providing feedback on performance. |
| Relatedness | Humans have a natural desire to connect with others and be part of a community. | The need for relatedness can be satisfied by gamification elements such as social interaction, collaboration, and competition. |
By incorporating these motivational theories into gamification design, creators can effectively engage and motivate users in various contexts.
Key Psychological Elements in Gamification
Gamification systems rely on several key psychological elements that stimulate motivation and engagement. Understanding these elements and how they work is essential for designing effective and successful gamification experiences.
Extrinsic Motivation
Extrinsic motivation refers to the drive to perform activities or complete tasks for external rewards or outcomes. Gamification often relies on extrinsic motivators to encourage users to engage with the system.
Rewards and Incentives
Rewards and tangible incentives are among the typical game design elements routinely used in gamification efforts. They provide users with a sense of achievement and progress, encouraging them to continue engaging with the activity.
Gamification systems employ various types of rewards, including points, badges, trophies, virtual currency, and unlockable content. Each type serves a different purpose and can be used to reinforce specific behaviors or actions.
The use of reward systems is a tried and tested approach, with numerous studies supporting their effectiveness in increasing motivation and engagement.
For instance, a review of empirical studies on gamification by Hamari, Koivisto, and Sarsa (2014) found that reward systems (and other game features) generally had a positive effect on the engagement and enjoyment of users.
Competition and Social Comparison
Competition is a powerful extrinsic motivator that drives many individuals to excel in their performance. In gamification, competitive elements such as leaderboards and rankings can encourage users to outperform their peers or surpass their personal bests.
Similarly, social comparison is another key element that drives motivation. Social comparison theory, first proposed by psychologist Leon Festinger in 1954, suggests that people evaluate their own abilities and opinions by comparing themselves to others. In gamification, social comparison can be facilitated through features such as public profiles, shared achievements, and collaborative challenges.
It’s important to remember that implementing leaderboards and rankings to capitalize on competition/social comparison needs to be done carefully. JMIR Serious Games journal’s study from 2021 suggested that improper use of these gamification elements may negatively impact the motivation and performance of some individuals.
To combat this, the study proposes a number of objectives that should be kept in mind when designing these features, such as minimizing the sense of inadequacy and prioritizing the sense of success to drive upward counterfactual thinking.
Intrinsic Motivation
Intrinsic motivation refers to the drive to engage in activities for their inherent enjoyment or satisfaction rather than for external rewards. Gamification designers aim to foster intrinsic motivation by creating engaging experiences that users find enjoyable and fulfilling.
Challenge and Skill Development
One key aspect of intrinsic motivation is the desire for challenge and skill development. People are naturally driven to improve their abilities and overcome difficulties. In gamification, this can be achieved by designing tasks or challenges that require users to develop new skills or apply existing ones in innovative ways.
To maximize motivation and engagement, it is essential to balance difficulty levels: tasks should be challenging enough to stimulate interest but not so difficult that they become frustrating or demoralizing. Research by Csikszentmihalyi (1990) on the concept of “flow” supports this idea, suggesting that game-like activities with flexible challenges are bound to be more enjoyable to users.

Curiosity and Exploration
Another key element of intrinsic motivation is curiosity, which drives individuals to seek out new experiences and learn new things. Gamification systems can encourage curiosity and exploration by providing opportunities for discovery, experimentation, and creativity.
For example, incorporating hidden rewards, branching storylines, or interactive environments can inspire users to explore the system and engage more deeply with the content. Another particular game design element useful in this case is the ‘clue’ mechanic – a staple of experiences aimed at driving curiosity.
Applying the Psychology of Gamification in Various Contexts
Gamification has been successfully applied in various contexts, ranging from education and workplace productivity to health and fitness. By understanding the psychological principles behind gamification, designers can create tailored experiences that effectively motivate and engage users in each of these domains.
Education and Learning
Gamification has shown great potential in enhancing student engagement and motivation to learn.
If you combine game design elements such as rewards, competition, challenge, and feedback, educational systems can experience a transformed earning experience – one that is highly enjoyable and stimulating.
Research has consistently demonstrated the effectiveness of gamification in education. For example, a meta-analysis conducted by Dicheva et al. (2015) found that most of the reviewed 34 papers reported positive impacts on students subjected to the gamified educational system – although more research is needed to understand the long-term effects.
A 2020 experiment conducted on a group of 40 undergraduate students showed a distinct improvement in the accuracy of those subjected to gamified learning – particularly individuals who were displaying low agreeableness and openness. This seems to suggest that gamification in educational contexts has a more substantial effect on introverted students than on their extroverted counterparts.

Workplace Productivity
Gamification can also be used to increase workplace productivity and motivation. By adding specific game design elements to work tasks, employers can encourage employees to perform at their best and meet organizational goals.
A 2017 comprehensive review of the research material on gamification suggested that gamified work environments were very conducive to higher levels of motivation and engagement and contributed to collaborative work and team performance.
The review took into account 35 different articles, ranging from quantitative, qualitative, and case studies to theoretical papers based on 17 independent samples – a very diverse and reliable selection.
Ensuring Long-Term Engagement and Motivation Through Gamification
While gamification can be highly beneficial to users, it is essential to consider how to maintain long-term motivation and engagement. Focusing too much on certain elements might endanger your gamification initiative and result in disappointing returns.
Avoiding Overemphasis on Extrinsic Rewards
While extrinsic rewards can be effective in motivating users, overreliance on these basic elements may lead to unintended consequences. Users who try to excel only for the sake of rewards may lose interest in improving themselves or completing the task once the rewards are no longer available.
They may also demand more and more satisfying rewards, leading to a feeling of entitlement. In extreme cases, users who have always experienced extrinsic motivation may have a harder time adapting to situations where rewards are not available.
Encouraging Intrinsic Motivation
To ensure long-term engagement, gamification designers should focus on fostering intrinsic motivation by incorporating elements that promote challenge, exploration, and skill development.
These elements can inspire users to continue using the system even when external rewards are no longer available, as the main drive behind their actions is the inherent enjoyment of the experience.
Adapting Gamification Strategies to Individual Differences
Individuals differ in their preferences and abilities. To maximize the motivation users get from gamified activities, designers need to consider these individual differences and create personalized experiences.
By tailoring gamification strategies to suit various learning styles, skill levels, and personality traits, designers can ensure that their systems are effective for a diverse range of users.
For example, some people may thrive on competition and social comparison, while others might prefer collaboration or solitary challenges. By offering multiple modes of engagement, gamification systems can cater to the unique needs and preferences of each user.
Aribo Helps Motivate by Gamifying Your Activities
The motivational power of gamified activities is significant, so it’s no wonder that many businesses, organizations, and individuals want to implement gamification into their own systems. However, it can be difficult to do so manually, especially if you are new to the concept. That’s where Aribo comes in.
Aribo is a gamification platform designed to help users gamify their activities and tasks in various contexts, such as education, HR, or tourism. Packed to the brim with features, Aribo makes it easy for users to add game-like elements to their experiences and track their progress. Whether you’re looking to create a more engaging learning environment or increase workplace productivity, Aribo can help you achieve your goals.
Sign up for Aribo today and motivate your users like never before!
Conclusion
Gamification has proven to be a powerful tool for motivating and engaging users across various contexts, such as education, workplace productivity, and personal growth.
By understanding the underlying psychological principles of motivation and incorporating key elements like extrinsic and intrinsic motivators, challenge, and exploration, designers can create gamified experiences that effectively drive users to achieve their goals.
As long as you keep the balance between extrinsic rewards and intrinsic motivation and cater to individual differences, gamification can lead to long-term success and satisfaction.
So why wait? Armed with this knowledge and tools like Aribo, you can start implementing gamification strategies in your own projects and unlock the full potential of motivation for yourself, your team, and your organization.
Embrace the power of gamification and watch as engagement and productivity soar to new heights!